User:Jahsonic/The linguistic sign is not arbitrary
From The Art and Popular Culture Encyclopedia
| Revision as of 22:13, 6 October 2013 Jahsonic (Talk | contribs) ← Previous diff |
Revision as of 22:15, 6 October 2013 Jahsonic (Talk | contribs) Next diff → |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
| But the [[linguistic sign]] is not [[arbitrary]]! | But the [[linguistic sign]] is not [[arbitrary]]! | ||
| - | Isn't the [[Bouba/kiki effect]] an instance of or proof of a [[universal language]] ruled by [[sound symbolism]]? | + | The proof: the [[Bouba/kiki effect]], an instance a [[universal language]] ruled by [[sound symbolism]]. |
| - | Not only does 95% of the [[informant]]s assign "kiki" to the [[angular]] shape and "bouba" to the [[curvilinear]] shape, informal research conducted by [[Jan Willem Geerinck|myself]] indicates that when informants are asked which of the two shapes is the '[[smart]]' one and which is the '[[dumb]]' one, "kiki" is usually designated as the smart one (remember, [[sharp]] in English also means [[intelligent]]) and "bouba" the dumb one (likewise, [[dull]] means not intelligent). | + | In the "Bouba/kiki" experiment, 95% of the [[informant]]s assigns "kiki" to the [[angular]] shape and "bouba" to the [[curvilinear]] shape. |
| + | |||
| + | Informal research conducted by [[Jan Willem Geerinck|myself]] indicates that when informants are asked which of the two shapes is the '[[smart]]' one and which is the '[[dumb]]' one, "kiki" is usually designated as the smart one (remember, [[sharp]] in English also means [[intelligent]]) and "bouba" the dumb one (likewise, [[dull]] means not intelligent). | ||
| This means that [[shape]]s can be connected both to [[sound]]s and to [[affect]]s. | This means that [[shape]]s can be connected both to [[sound]]s and to [[affect]]s. | ||
Revision as of 22:15, 6 October 2013
|
Related e |
|
Featured: |
At the beginning of the 20th century, the Swiss linguist Ferdinand de Saussure in his canonical Course in General Linguistics (1916) stated that:
- The bond between the signifier and the signified is arbitrary. Since I mean by sign the whole that results from the associating of the signifier with the signified, I can simply say: the linguistic sign is arbitrary. [1]source
These findings have implications for the evolution of language, because it suggests that the naming of objects is arbitrary and not dependent on sound symbolism.
But the linguistic sign is not arbitrary!
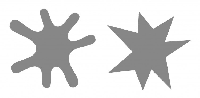
The proof: the Bouba/kiki effect, an instance a universal language ruled by sound symbolism.
In the "Bouba/kiki" experiment, 95% of the informants assigns "kiki" to the angular shape and "bouba" to the curvilinear shape.
Informal research conducted by myself indicates that when informants are asked which of the two shapes is the 'smart' one and which is the 'dumb' one, "kiki" is usually designated as the smart one (remember, sharp in English also means intelligent) and "bouba" the dumb one (likewise, dull means not intelligent).
This means that shapes can be connected both to sounds and to affects.
I was surprised not to see the Bouba/kiki effect in The Search for the Perfect Language (The Making of Europe) by Umberto Eco.
See also


